| Identification |
| Name: | Benzenesulfonamide,N-[(butylamino)carbonyl]-4-methyl- |
| Synonyms: | Urea,1-butyl-3-(p-tolylsulfonyl)- (8CI);1-Butyl-3-(p-methylphenylsulfonyl)urea;1-Butyl-3-(p-tolylsulfonyl)urea;3-(p-Tolyl-4-sulfonyl)-1-butylurea;Aglicid;Arkozal;Artosin;Artozin;Butamid;Butamide;D 860;Diaben;Diabetamid;Diabetol;Diabuton;Diasulfon;Dolipol;Glyconon;HLS 831;Ipoglicone;Mobenol;N-(4-Methylbenzenesulfonyl)-N'-butylurea;N-(4-Methylphenylsulfonyl)-N'-butylurea;N-(Sulfonyl-p-methylbenzene)-N'-n-butylurea;N-(p-Methylbenzenesulfonyl)-N'-butylurea;N-(p-Tolylsulfonyl)-N'-butylcarbamide;N-Butyl-N'-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)urea;N-Butyl-N'-(p-tolylsulfonyl)urea;N-Butyl-N'-p-toluenesulfonylurea;N-n-Butyl-N'-tosylurea;NSC 23813;NSC 87833;Orabet;Oralin;Orezan;Orinase;Orinaz;Oterben;Pramidex;Rastinon;Tolbusal;Tolbutamid;Tolbutamide;Toluina;Tolumid;Tolumide;Toluvan;U 2043;Willbutamide; |
| CAS: | 64-77-7 |
| EINECS: | 200-594-3 |
| Molecular Formula: | C12H18N2O3S |
| Molecular Weight: | 270.38 |
| InChI: | InChI=1/C12H18N2O3S/c1-3-4-9-13-12(15)14-18(16,17)11-7-5-10(2)6-8-11/h5-8H,3-4,9H2,1-2H3,(H2,13,14,15) |
| Molecular Structure: |
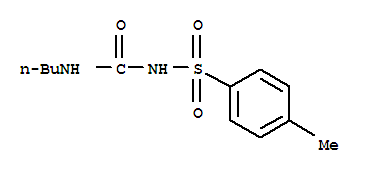 |
| Properties |
| Melting Point: | 128-130°C |
| Boiling Point: | white crystalline powder |
| Density: | 1.184 g/cm3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. |
| Solubility: | DISSOLVES READILY IN AQ NAOH TO FORM SODIUM DERIV
SOL IN ETHANOL, CHLOROFORM; FREELY IN DIMETHYL CARBONATE; INSOL IN WATER
Sol in ethanol, ethyl ether, and chloroform.
In water, 109 mg/l @ 37 deg C |
| Appearance: | white crystalline powder |
| Specification: |
The chemical synonyms of 1-Butyl-3-(4-methylphenyl)sulfonylurea (64-77-7) are Labotest-bb lt00772316 ; 3-[P-tolyl-4-sulfonyl]-1-butylurea ; 1-Butyl-3-(p-tolylsulfonyl)urea ; 1-Butyl-3-(4-methylbenzenesulfonyl)urea ; 1-Butyl-3-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)urea ; 1-N-butyl-3-(p-tolylsulfonyl)urea ; Toluina ; Tolbutamide .Tolbutamide is an amide. Amides/imides react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides/imides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases. Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
|
| Report: |
NCI Carcinogenesis Bioassay (feed); No Evidence: mouse, rat NCITR* National Cancer Institute Carcinogenesis Technical Report Series. (Bethesda, MD 20014) No. NCI-CG-TR-31 (1977). . Reported in EPA TSCA Inventory. EPA Genetic Toxicology Program.
|
| Storage Temperature: | Refrigerator |
| Color: | WHITE OR PRACTICALLY WHITE CRYSTALLINE POWDER
Crystals |
| Usage: | An antidiabetic, used as a hypoglycemic agent in veterinary medicine. |
| Safety Data |
| |
 |