| Identification |
| Name: | D-Glucose, 4-O-a-D-glucopyranosyl- |
| Synonyms: | Maltose(8CI);4-O-a-D-Glucopyranosyl-D-glucose;Advantose 100;D-(+)-Maltose;D-Maltose;Finetose;Finetose F;Flolys D 5780;MP 21;Malt sugar;Maltose HH;Maltose HHH;Maltose OM;Sunmalt;Sunmalt S; |
| CAS: | 69-79-4 |
| EINECS: | 200-716-5 |
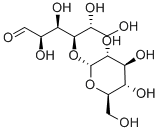
| Molecular Formula: | C12H22O11 |
| Molecular Weight: | 342.3 |
| InChI: | InChI=1/C12H22O11/c13-1-3-5(15)6(16)9(19)12(22-3)23-10-4(2-14)21-11(20)8(18)7(10)17/h3-20H,1-2H2/t3-,4-,5-,6+,7-,8-,9-,10-,11-,12-/m1/s1 |
| Molecular Structure: |
 |
| Properties |
| Flash Point: | 357.8°C |
| Boiling Point: | 667.9°C at 760 mmHg |
| Density: | 1.76g/cm3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Refractive index: | n20/D 1.361 |
| Appearance: | colourless crystals or white powder |
| Specification: |
Maltose (69-79-4), or malt sugar, is a disaccharide formed from two units of glucose joined with an α(1→4) linkage. It is the second member of an important biochemical series of glucose chains. The addition of another glucose unit yields maltotriose ; further additions will produce dextrins and eventually starch.It can be broken down into two glucose molecules by hydrolysis. In living organisms, the enzyme maltase can achieve this very rapidly. In the laboratory, heating with a strong acid for several minutes will produce the same result.The production of maltose from germinating cereals, such as barley, is an important part of the brewing process. When barley is malted, it is brought into a condition in which the concentration of maltose-producing amylases has been maximized. Mashing is the process by which these amylases convert the cereal's starches into maltose. Metabolism of maltose by yeast during fermentation then leads to the production of ethanol and carbon dioxide.
|
| Report: |
Reported in EPA TSCA Inventory.
|
| Flash Point: | 357.8°C |
| Safety Data |
| |
 |