| Identification |
| Name: | Arsinic acid,As,As-dimethyl- |
| Synonyms: | Arsineoxide, hydroxydimethyl- (7CI,8CI); Arsinic acid, dimethyl- (9CI); Cacodylicacid (6CI); Ansar 138; Arsan; Dimethylarsenic acid; Dimethylarsinic acid;Hydroxydimethylarsine oxide; NSC 103115; NSC 71157; NSC 71158; Phytar; Silvisar510; Sylvicor |
| CAS: | 75-60-5 |
| EINECS: | 200-883-4 |
| Molecular Formula: | C2H7 As O2 |
| Molecular Weight: | 137.9974 |
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C2H7AsO2/c1-3(2,4)5/h1-2H3,(H,4,5) |
| Molecular Structure: |
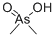 |
| Properties |
| Transport: | UN 1572 6 |
| Stability: | Aqueous solutions react violently with active metals. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases. |
| Solubility: | very soluble Stability Aqueous solutions react violently with active metals.Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases.Toxicology Highly toxic by inhalation, ingestion and through skin contact.May cau |
| Appearance: | colorless or white crystalline powder |
| Specification: |
General description about Cacodylic Acid (CAS NO.75-60-5) , it is a colorless, odorless crystalline solid.Toxic by ingestion and irritating to skin and eyes.
Air & Water Reactions: Hygroscopic. Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile: It is a weak acid. Dissolves in water to yield solutions containing more hydrogen ions than pure water contains and so having a pH less than 7.0. Is neutralized exothermically by all bases to produce water plus a salt. Reacts (but usually slowly) with active metals to form gaseous hydrogen and a metal salt. Such reactions occur in principle for the solid acid but are quite slow if the solid acid remains dry. The solid may absorb enough water from the air and dissolve sufficiently in it to corrode or dissolve iron, steel, and aluminum parts and containers. Reacts with cyanide salts to generate gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Flammable and/or toxic gases and heat may be generated with diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides. Also may react with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), to generate flammable and/or toxic gases and heat. Reaction with carbonates and bicarbonates generates a harmless gas (carbon dioxide) but still some heat. Can be oxidized exothermically by strong oxidizing agents and reduced by strong reducing agents; a wide variety of products is possible. May initiate polymerization reactions; may catalyze (increase the rate of) chemical reactions.
Health Hazard: Chemical is essentially non-irritating in contact with skin or eyes. Ingestion causes arsenic poisoning, but symptoms are delayed.
Fire Hazard: Behavior in Fire: May form toxic oxides of arsenic when heated.
|
| Report: |
IARC Cancer Review: Animal Inadequate Evidence IMEMDT IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Man . 23 , 1980,p. 39.(World Health Organization, Internation Agency for Research on Cancer,Lyon, France.: ) (Single copies can be ordered from WHO Publications Centre U.S.A., 49 Sheridan Avenue, Albany, NY 12210) . Arsenic and its compounds are on the Community Right-To-Know List. Reported in EPA TSCA Inventory. EPA Genetic Toxicology Program.
|
| Packinggroup: | II |
| Storage Temperature: | Store at RT. |
| Sensitive: | Hygroscopic |
| Color: | Crystals from alcohol and ether
Colorless
TRICLINIC CRYSTALS
White; water solutions may be dyed blue |
| Usage: | Cacodylic acid is used for dermatologic treatment in cronic eczema, anemia and as a tonic. |
| Safety Data |
| |
 |