| Identification |
| Name: | Carbamothioic acid,N,N-dipropyl-, S-(phenylmethyl) ester |
| Synonyms: | Carbamicacid, dipropylthio-, S-benzyl ester (7CI); Carbamothioic acid, dipropyl-,S-(phenylmethyl) ester (9CI); Arkade; Benzyl dipropylthiolcarbamate; Boxer;Boxer (ICI Agrochemicals); Defi; Prosulfocarb; R 15574; S-BenzylN,N-dipropylthiocarbamate; S-Benzyl dipropylthiocarbamate; S-Benzyldipropylthiolcarbamate; SC 0574 |
| CAS: | 52888-80-9 |
| EINECS: | 401-730-6 |
| Molecular Formula: | C14H21 N O S |
| Molecular Weight: | 251.42 |
| InChI: | InChI=1/C14H21NOS/c1-3-10-15(11-4-2)14(16)17-12-13-8-6-5-7-9-13/h5-9H,3-4,10-12H2,1-2H3 |
| Molecular Structure: |
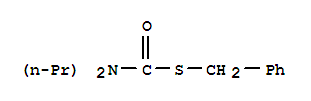 |
| Properties |
| Transport: | UN 3082 |
| Flash Point: | 167.1°C |
| Boiling Point: | 352.6°Cat760mmHg |
| Density: | 1.049g/cm3 |
| Refractive index: | 1.541 |
| Water Solubility: | 13 mg l-1 |
| Specification: |
Air & Water Reactions :Thio and dithiocarbamates slowly decompose in aqueous solution to form carbon disulfide and methylamine or other amines. Such decompositions are accelerated by acids.
Reactivity Profile: S-(Phenylmethyl) dipropylcarbamothioate (CAS NO. 52888-80-9) is a thiocarbamate. Flammable gases are generated by the combination of thiocarbamates and dithiocarbamates with aldehydes, nitrides, and hydrides. Thiocarbamates and dithiocarbamates are incompatible with acids, peroxides, and acid halides.
|
| Flash Point: | 167.1°C |
| Safety Data |
| |
 |